NGINX on Linux
Install NGINX on Debian, Ubuntu, and Linux Mint
Open a terminal and use the following commands to install NGINX on Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Kali, and other Debian or Ubuntu derivatives.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install nginx
Install NGINX on Fedora, CentOS, and Red Hat
Open a terminal and use the following commands to install NGINX on Fedora, CentOS, Red Hat, and other Fedora or Red Hat derivatives.
$ sudo dnf upgrade
$ sudo dnf install nginx
Install NGINX on Arch Linux and Manjaro
Open a terminal and use the following commands to install NGINX on Arch Linux, Manjaro, and other Arch derivatives.
$ sudo pacman -Syu
$ sudo pacman -S nginx
Manage NGINX
Most Linux distributions, including all from the previous section, will use systemd to manage the NGINX service. Use the following commands to manage it on your system.
Check the status of NGINX (i.e. see if it’s running):
$ systemctl status nginx
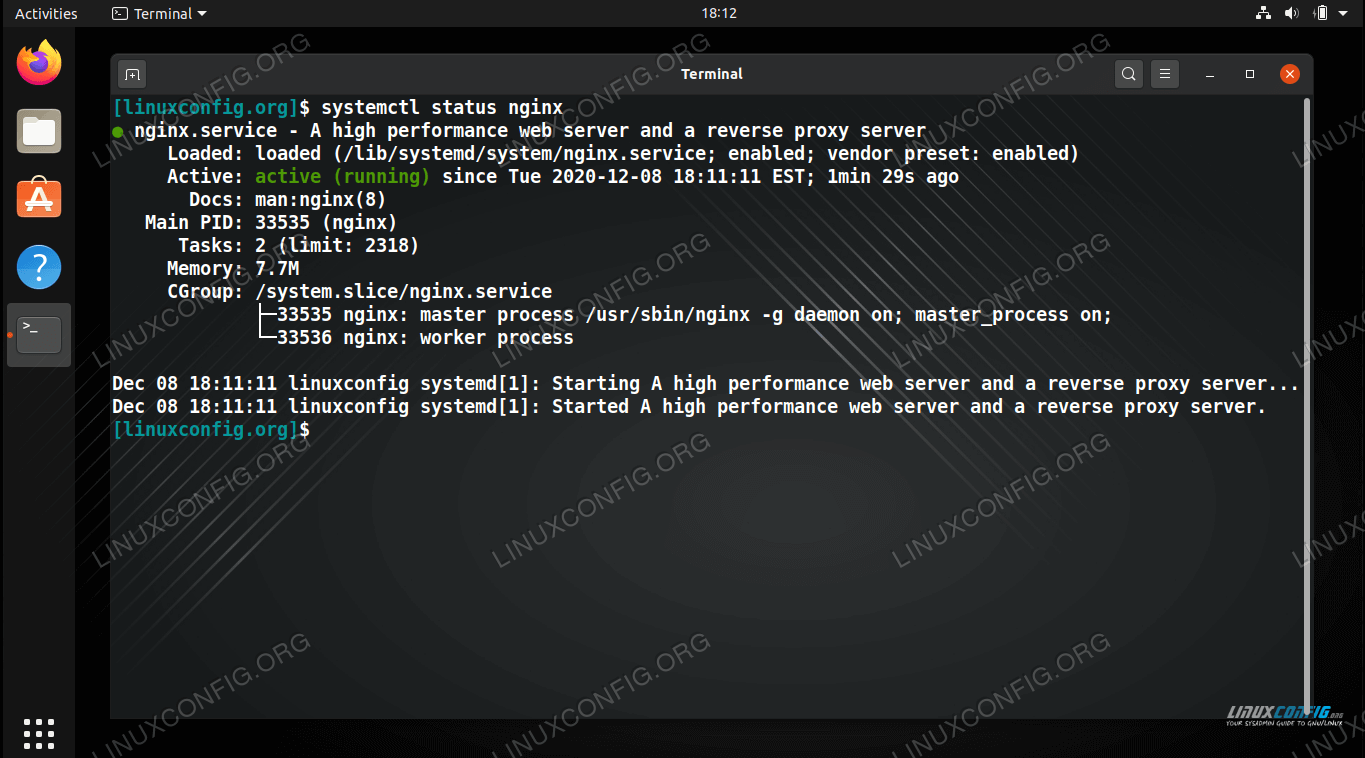
Checking the status NGINX service
Start or stop NGINX:
$ sudo systemctl start nginx
AND
$ sudo systemctl stop nginx
Enable or disable NGINX from starting automatically upon system boot:
$ sudo systemctl enable nginx
AND
$ sudo systemctl disable nginx
Reload or Restart NGINX– reload will just reload configuration files, whereas restart will restart the service entirely:
$ sudo systemctl reload nginx
AND
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Check the NGINX configuration files for errors – especially helpful before committing changes in a production environment:
$ sudo nginx -t
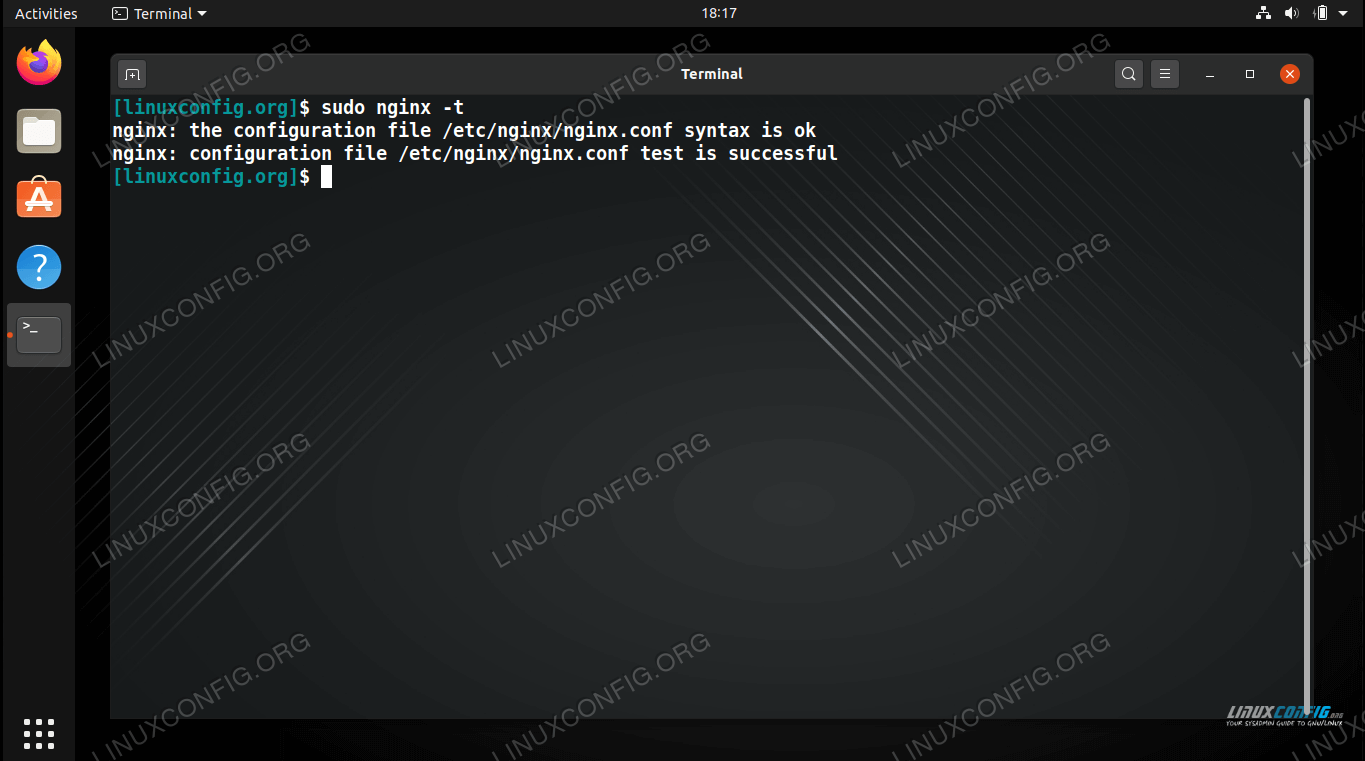
Checking NGINX configuration files for syntax errors
Closing Thoughts
In this tutorial, we saw how to install NGINX on a variety of popular Linux distributions. We also learned how to manage the service with systemd, and check the configuration files for syntax errors. These instructions should be enough to get the software up and running. You can continue with our other guides to setup NGINX as a web server or reverse proxy server.